
(a)
Interpretation:
Bond angle has to be predicted using VSEPR model for the given structure and also the hybrid orbitals on the central atoms has to be given. The molecule is polar or not also has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure is used for predicting the shape of molecules. From the steric number obtained in a Lewis structure, the molecular geometry can be predicted. VSEPR model can predict the shape of molecules considering their Lewis structure. Certain rules has to be followed in for the VSEPR model.
- The molecule will have a shape where there is minimal electrostatic repulsion between the valence‑shell electron pairs.
- The forces of repulsion between two lone pairs of electrons will be higher than the repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of electrons. This in turn will be higher than the bond pair‑bond pair of electrons.
The hybridized orbitals and the steric number can be related as shown below;
| Steric number | Hybridized orbital |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 |
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Resonance structure:
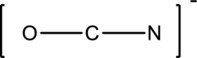
The given species is shown below;
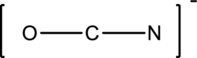
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
A total of
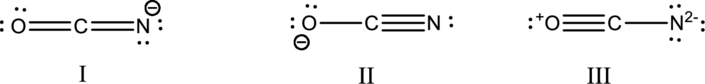
Hybrid orbitals of central atoms in structure I:
The resonance structure is shown below;
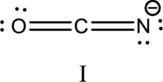
Hybrid orbitals of central carbon atom:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to two atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the hybridization of carbon atom is
Hybrid orbitals of central atoms in structure II:
The resonance structure is shown below;
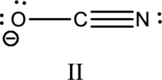
Hybrid orbitals of central carbon atom:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to two atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the hybridization of carbon atom is
Hybrid orbitals of central atoms in structure III:
The resonance structure is shown below;
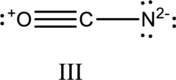
Hybrid orbitals of central carbon atom:
The carbon atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to two atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the hybridization of carbon atom is
All the resonance structure have the same hybrid orbitals in the central atom.
(b)
Interpretation:
Bond angle has to be predicted using VSEPR model for the given structure and also the hybrid orbitals on the central atoms has to be given. The molecule is polar or not also has to be indicated.
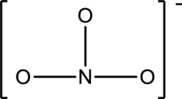
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Resonance structure:
The given species is shown below;
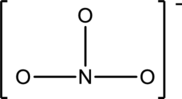
The total number of valence electrons is calculated as shown below;
A total of
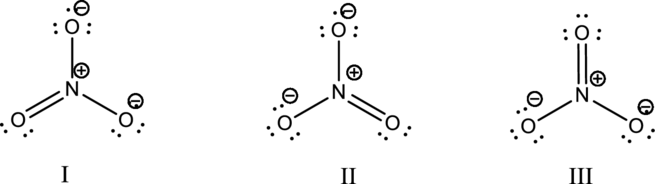
Hybrid orbitals of central atoms in structure I:
The resonance structure is shown below;
Hybrid orbitals of central nitrogen atom:
The nitrogen atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to three atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the hybridization of nitrogen atom is
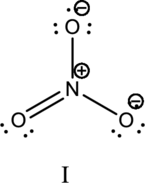
Hybrid orbitals of central atoms in structure II:
The resonance structure is shown below;
Hybrid orbitals of central nitrogen atom:
The nitrogen atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to three atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the hybridization of nitrogen atom is
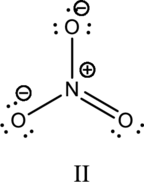
Hybrid orbitals of central atoms in structure III:
The resonance structure is shown below;
Hybrid orbitals of central nitrogen atom:
The nitrogen atom has does not have a lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to three atoms. Therefore, the steric number is calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, the hybridization of nitrogen atom is
All the resonance structure have the same hybrid orbitals in the central atom.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- It is possible to write a simple Lewis structure for the SO42- ion, involving only single bonds, which follows the octet rule. However, Linus Pauling and others have suggested an alternative structure, involving double bonds, in which the sulfur atom is surrounded by six electron pairs. (a) Draw the two Lewis structures. (b) What geometries are predicted for the two structures? (c) What is the hybridization of sulfur in each case? (d) What are the formal charges of the atoms in the two structures?arrow_forwardThe structure of caffeine is shown below. (a) Complete the Lewis structure. (b) How many pi bonds are present in caffeine? How many sigma bonds? (c) Identify the hybridization of the carbon atoms. (d) What is the value of the O-C-N angle?arrow_forwardThe Lewis structure of BH2Cl (a) Is the molecule polar or nonpolar? (b) What is the hybridization of the carbon atom? (c) What is the geometric shape of the molecule?arrow_forward
- 7. Nitrogen is the central atom in each of the species given. (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structure for each of the species. + NO₂ NO₂ NO₂ (b) List the species in order of increasing bond angle. Justify your answer. (c) For NO₂ and NO₂, give the hybridization of the nitrogen atom in it. (d) Identify the only one of the species that dimerizes and explain what causes it to do so.arrow_forwardWrite the best Lewis dot structure for POCl₃, be sure to give the electronic geometry, molecular geometry, hybridization of the central element, polarity, and bond angle around the central element.arrow_forward1. For each molecular geometry, give the number of total electron pairs, the number of bonding pairs and the number of lone pairs on the central atom. (a) (b) (c) 2. For the following species provide the Lewis structure and make a 3D sketch showing estimated bond angles. Determine the polarity of each molecular and draw the dipole. a) SF4 b) KrF4 3. Determine the 3D structure of the molecule of formula C2H4O (H3CCHO). Indicate the geometry around each "central" atom and estimate bond angles. Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper X-A-X XX Linear Trigonal planar Bent Tetrahedral Trigonal pyramidal Trigonal bipyramidal Seesaw Octahedral Square planararrow_forward
- . Assume that the third-period element phosphorus forms a diatomic molecule, P2, in an analogous way as nitrogen does to form N2. (a) Write the electronic configuration for P2. Use [Ne2] to represent the electron configuration for the first two periods. (b) Calculate its bond order. (c) What are its magnetic properties (diamagnetic or paramagnetic)?arrow_forward2(a) Provide the Lewis structures for both CH3OH and C2H3Cl. 2(b) What is the largest bond angle among all the bond angles in CH3OH and C2H3Cl? Listthe three atoms making this largest bond angle, and estimate the value of the angle.2(c) What intermolecular forces are present(i) between CH3OH molecules?(ii) between C2H3Cl molecules?arrow_forward(a) Find the angle u between adjacent nearest-neighbor bonds in the silicon lattice. Recall that each silicon atom is bonded to four of its nearest neighbors.The four neighbors form a regular tetrahedron— a pyramid whose sides and base are equilateral triangles. (b) Find the bond length, given that the atoms at the corners of the tetrahedron are 388 pm apart.arrow_forward
- 2. Consider the following molecules or ions: CIOF5, NOBr, NH2F, and XeO2F3+. Answer the following questions based on the Lewis structures and VSEPR theory prediction of their molecular shapes. (a) Which one has only bond angles of 109.5°? (b) Which one has only bond angles of 120°? (c) Which one has bond angles of 90 and 180°? (d) Which one has bond angles of 90, 120, and 180°?arrow_forward1A2: Define electron pair domain (EPD), count EPDS on building blocks, and use EPD knowledge to determine 3D geometry and bond angles of a tetrahedral, trigonal planar, linear building block. For the indicated atoms (look for the arrows) in each of the given structures: (a) state how many EPDs are present; (b) Label tetrahedral atoms with "TET," trigonal planar atoms with "TP," and linear atoms with "LIN;" (c) Identify one (1) indicated atom in each structure for which resonance structures bring a change in the number of EPDs from 4++3/3+4 or 3+2/2+3. A resonance structure must be reported to justify your reported EPD changes. H₂C CH3 --С HO 1 Br -CH3 CH3 CI H₂C N CH3 CH3 он оarrow_forwardDescribe the bond angles to be found in each of the following molecular structures: (a) trigonal planar, (b) tetrahedral, (c) octahedral, (d) linear.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning


