
Concept explainers
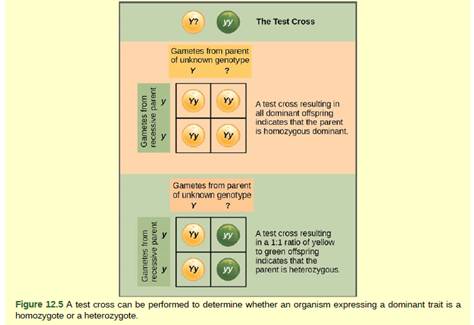
Figure 12.5 In pea plants, round peas (R) are dominant to wrinkled peas (r). You do a test cross between a pea plant with wrinkled peas (genotype rr) and a plant of unknown genotype that has round peas. You end up with three plants, all which have round peas. From this data, can you tell if the round pea parent plant is homozygous dominant or heterozygous? If the round pea parent plant is heterozygous, what is the probability that a random sample of 3 progeny peas will all be round?
To write:
The probability that a random sample of 3 progeny peas will be round.
Introduction:
The test cross can be defined as the cross, which is used to determine the genotype of the plants, especially, whether it is heterozygous dominant or homozygous dominant. In case the result of test cross comes as all dominant, then the plant is homozygous dominant, in case the cross shows 1:1 phenotype of dominant: recessive then the plant tested would be heterozygous dominant.
Explanation of Solution
The question says that a round seed pea plant was crossed with recessive (wrinkled seed) pea plant, which gives three plant having round pea seeds.
The given below is the analysis of the heterozygous pea plant and homozygous pea plant with a wrinkled plant.
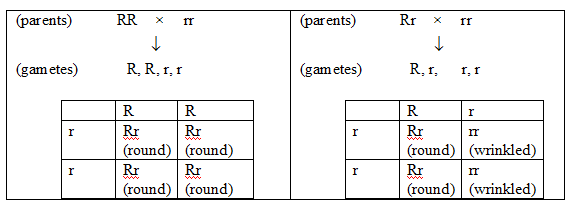
From the crosses shown above, we can observe that in a test cross, the homozygous dominant plant produces all heterozygous dominant plants and the heterozygous plant produces 50% dominant and 50% recessive.
The transfer of the allele is random, as there is a probability that the plant with homozygous dominant trait would also produce the round seed, the data given in the question is very small. Hence, it cannot be concluded that the parent is homozygous or heterozygous. But, as per the given data one can most probably say it is homozygous.
For a heterozygote plant, the probability of getting one plant having round seed is 50% or ½.
Hence, the probability of getting 3 plant with a round seed with heterozygote plant would be:
The tested plant can be both homozygous or heterozygous and the probability of getting 3 plant with round seed by the heterozygous plant is 1/8.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Biology 2e
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- You want to determine whether genes a and b are linked. What cross would you use and why? How would this cross tell you if they are linked?arrow_forwardImagine that you are performing a cross involving seed color in garden pea plants. What traits would you expect to observe in the F1 offspring if you cross true-breeding parents with green seeds and yellow seeds? Yellow seed color is dominant over green. a. only yellow-green seeds b. only yellow seeds c. 1:1 yellow seeds:green seeds d. 1:3 green seeds:yellow seedsarrow_forwardYou have a purple-flowered pea plant, but you do not know if it is homozygous (PP) or heterozygous (Pp) for flower color because both genotypes result in the same purple phenotype. Purple color allel (P) is dominant over white flower allel (p). What would you do to determine the genotype of flower color of this plant? Lötfen birini seçin: O a. Crossing the plant with homozygous large flowered pea plant (LL) Ob. Crossing the plant with heterozygous purple flowered pea plant (Pp) Crossing the plant with homozygous dominant purple flowered pea plant (PP) d. Crossing the plant with a plant whose genotype is unknown e. Crossing the plant with homozygous recessive white flowered pea plant (pp)arrow_forward
- Imagine you are Performing a cross involving seed color in garden pea plants. What F1 offspring would you expect if you cross true-breeding parents with green seeds and yellow seeds? Yellow seed color is dominant over green.arrow_forwardIn corn, two independent, recessive nuclear genes, japonica (j) and iojap (ij), produce variegation (green and white striped leaves). Matings between individuals heterozygous for japonica always produce 3 green:1 striped individuals regardless of how the cross is performed. You have a variegated plant that could be either jj or ijij . What cross can you make to determine the genotype of this plant, and what results do you expect in the F1 generation in each case?arrow_forwardIn pea plants yellow seed color, (GG) and round seed shape (WW) seeds are dominant traits, while green color or (gg) wrinkled shape (ww) seeds are recessive traits. You cross a pure breeding plant with yellow wrinkled seeds to a pure breeding plant with green round seeds to generate F1s. When you perform a reciprocal cross you get the same results. If you perform a test cross on a female from the F1 generation, what outcome do you expect in the offspring? a) 4 phenotypes in equal proportions b) 4 phenotypes in unequal proportions c) 2 phenotypes in equal proportions d) 8 phenotypes in unequal proportions e) None of the abovearrow_forward
- In corn plants, two pairs of genes control color in the ears of corn. The following genotypes result in various colors: W-C- [red]; wwC- [yellow]; W-cc [white]; wwcc [white]. What is the phenotypic ratio of the dihybrid cross between corn plants heterozygous for both genes? (Dashes mean the allele could be W or w)arrow_forwardThree recessive traits in garden pea plants are as follows: yellow pods are recessive to green pods, bluish green seedlings are recessive to green seedlings, creeper (a plant that cannot stand up) is recessive to normal. A true breeding normal plant with green pods and green seedlings was crossed to a creeper with yellow pods and bluish green seedlings. The F1 plants were then crossed to creepers with yellow pods and bluish green seedlings. The following results were obtained for the F2 offspring: 2059 green pods, green seedlings, normal 151 green pods, green seedlings, creeper 281 green pods, bluish green seedlings, normal 15 green pods, bluish green seedlings, creeper 2041 yellow pods, bluish green seedlings, creeper 157 yellow pods, bluish green seedlings, normal 282 yellow pods, green seedlings, creeper 11 yellow pods green seedlings, normal Construct a genetic map that shows the…arrow_forwardFigure 8.10 In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white (p), and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green (y). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PpYY and ppYy pea plants? How many squares would you need to complete a Punnett square analysis of this cross?arrow_forward
- In corn plants, two pairs of genes control color in the ears of corn. The following genotypes result in various colors: W-C- [red]; wwC- [yellow]; W-cc [white]; wwcc [white]. What is the phenotypic ratio of the dihybrid cross between corn plants heterozygous for both genes? (Dashes mean the allele could be W or w, i.e., WWCC/WwCC/WWCc/WwCc geneotype gives red color)arrow_forwardIn the video game Animal Crossing: New Horizons, flowering breeding is based in genetics. Each flower's color is determined by the genotype at three or four unlinked genes: R, Y, W, and S. The genotype of the elusive blue rose is RR YY ww ss. In the game, one way to get a blue rose is to cross two roses with the Rr Yy Ww ss genotype. A) What types of gametes and in what proportions will a Rr Yy Ww ss rose produce? B) In a cross Rr Yy Ww ss x Rr Yy Ww ss what are the possible offspring genotypes and at what frequency will they each appear? Show your work. C) What proportion of the offspring of the cross will be blue roses?arrow_forwardA pea plant has a mendilian completely dominant gene for height flower colour phenotype. A pure breeding tall purple flower plant is crossed with a white dwarf plant. All offspring are purple and tall. If one of these offspring are crossed again with the white dwarf plant, what is the chances of producing a tall white flower? Explain your answer and any assumptions that you had to make. Note: You may not need the entire punnett square below or you may wish to use a different method.arrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

