
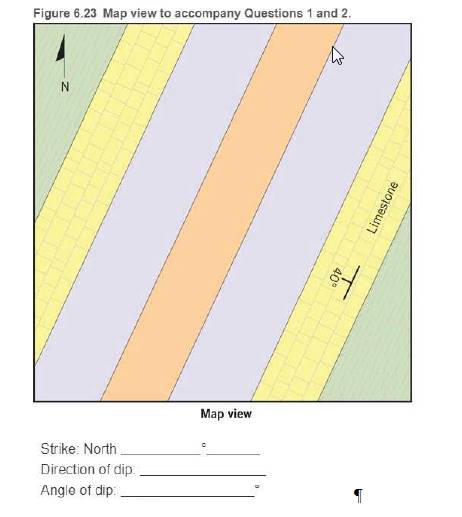
Refer to Figure 6.23 to describe the strike and dip of the limestone layer
Introduction:
The sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments that are transported by running water to the shallow seas, and over time they undergo processes like compression, compaction, burial, and cementation in the deep crust to form sedimentary rocks.
Answer to Problem 1LR
Correct answer:
The strike in the given limestone layer is 25 ° East. The direction of dip is 180 °, and the angle of dip is 40°.
Explanation of Solution
The method of calculating the strike, angle of dip, and direction of dip includes the measurement of strike and dip present on the rock layers or planar features. The strike in limestone is defined as the compass direction that is relative to north. It is constructed of the line formed by the intersection of a rock layer. The strike of the limestone layer is 25 ° East, the direction of dip is 180 °, and the angle of dip is 40°.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
APPLICATIONS+INVESTIGATIONS IN EARTH
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (8th Edition)
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
Microbiology: An Introduction
- What is the slope of the line?arrow_forwardPlease step by step solltionarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is correct with respect to a Gantt chart?a. The x-axis of a Gantt chart shows a time line.b. The y-axis shows the activities of a project.c. The Gantt chart itself does not show all dependencies among activities.d. The Gantt chart is named after 19th-century industrialist Henry Gantt.e. All of these statements are correct.arrow_forward
 Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
