
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation: Each number and the most acidic hydrogen in below molecule should be determined.
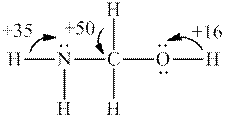
Concept introduction: Electronegative elements have tendency to attract electrons towards it. Since electrons are shared more towards electronegative element, it acquires partial negative charge on it. As a result, other bonded atom develops partial positive charge. Polarization in any molecule arises due to electronegativity difference between bonded atoms. Polarization that is caused by electronegative atom can induce polarization in neighboring bonds to very small extent. This effect is known as inductive effect. Due to this effect, hydrogen attached to positive atom become more acidic than that on neutral atom. This also explains more acidic nature of hydrogens attached to electronegative atoms as compared to other atoms.
b)
Interpretation: Whether the most acidic hydrogen in below structure is consistent with fact that this molecule has
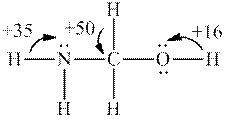
Concept introduction:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- For each molecule below, draw the conjugate acid or conjugate base or both if the molecule hasboth a conjugate acid and a conjugate base (e.g., water).arrow_forward=) - For each of the following molecules, identify (draw/mark) the most acidic proton. 02Narrow_forwardAde ed arrows to show the Arte attack the proton of the acid (breaking the X-H bond * Identify the nucleophile and electrophile ectants but the charge will be on a different molecule.) Circle the conjugate base. charges of any lons OK a) HO, b) кон SH c) NO. ONa HO + Approximate pK, values of Important organic functional groups pk, Protonated Cacborylic alcohol R. -2 5. 10 Phenol 16 Alcohol 25 Alkyne 38 Amine acid 44 Alkene 50 1. H OH R-OH R -H Alkane R. R. он R H ROH Protonated N amine H. H Thiol R-SHarrow_forward
- Examine the molecules below. Which site is most basic? Which H is most acidic? Highlight this site. Highlight this H. H :S- H. :O:arrow_forwardwhich is more acidic, carboxylic acids or phenols? How did you arrive at this conclusion? do not copy from google, i will downvotearrow_forward12. While each molecule below has more protons (H-atoms) than being shown, just focus on the protons identified. Compare the two protons identified. 1) Draw the two conjugate bases that could possibly result (althou gh one will be preferred over the other). The purpose here is to make you look at the conjugate base and the atom upon which the negative charge resides, then you should consider your SERIO factors. 2) Identify which proton is more acidic by circling the H, or H, on the original molecule. 3) Explain why by comparing the conjugate bases. Cirele the factor you considered when comparing the stabilities of the conjugate bases. Explanation: Size Electronegativity Resonance Inductive effect Orbital hybridization СвА св, Explanation: Size Electronegativity Resonance Inductive effect Orbital hybridization св, св,arrow_forward
- Br NH₂ OH NH₂ CH3 A/RO/exception Circle the more acidic compound and determine the effect responsible for such observation using ARIO methods, or if its an exception to the rule. Please explain thanks.arrow_forward3. Which one of the following answers represents the order of increasing bacisity for compounds the box? (1) CH;CH,ONa (2) (CH)NNa (3) сH,СО,Na O 2 weakest base) <1« 3 (strongest base) O 1 weakest base) «3+2 (strongest base) O 3 (weakest basel « 21 (strongest base) O 3 weakest base) < 1< 2 strongest base) Question 4 4. Which one of the following compounds has pka with the highest numeric value? HCI CH3NH2 CH3OH CH3Br CHllr HCI O CHNH2 O CHJOHarrow_forwardDraw the organic product of the Lewis acid-base reaction shown below. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate.arrow_forward
- Select the stronger base and then draw its conjugate acid below. CICH₂CH₂O or CH3CH₂O- • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • You do not have to include lone pairs in your answer. Ⓡ OO. n[1] ? ChemDoodlearrow_forward4)Label the following Lewis acid and Lewis base and draw Lewis structures showing the mechanism using curved arrows. a) F + BF3 → BF4 b) NH3 + HBr ➜ NH4+ Br-arrow_forwardWhat is/are the most acidic proton() in the moloecle below? Select the anneer where the most acidic proton(s) are circled 0.00 C A H₂ CH₂ che de ch (H₂) D CH₂arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
