
Draw a ray diagram that shows how to determine the location of the image that you observed above. Your diagram need not be drawn exactly to scale, but should correctly show the location of the object relative to the observer and to the lens and its focal points.
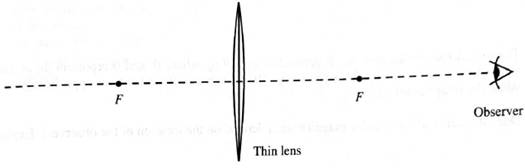
1. On the basis of your ray diagram, which is farther from the observer: the image or the object?
Is your answer consistent with your observations from pan A? If not, resolve the inconsistency.
2. Does a magnifying glass simply make an object appear closer (i.e., does it simply form an image of the object that is closer to you than the object itself)? If not, what does it do?
3. How can you tell from your ray diagram which would appear larger: the image of the pencil (with the lens in place) or the pencil (with the lens removed)?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Conceptual Integrated Science
University Physics Volume 1
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
- Use the ray diagramming technique to describe the image formed by concave and convex lenses at different positions using S-O-L-T (Size, Orientation, Location, and Type). Use the following measurement: focal length 1.5 cm, and height of object = 2.0 cm. Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. LOCATION OF THE OBJECT Convex Lens SIZE ORIENTATION LOCATION TYPE A. At C 1. 2. 3. 4. B. Beyond C C. Between F and C 6. 10. 8. 12. 5. 7. 9. 11. D. At F 13. 14. 15. 16. Е. Between and 17. 18. 19. 20. mirror Concave Len F. At C G. Beyond C 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. H. Between F' and C 29. 30. 31. 32. I. At F' J. 33. 34. 35. 36. Between F' and 37. 38. 39. 40. mirrorarrow_forwardSolve with illustration. Locate the image by tracing it through ray diagramming and answer three questions for the possible positions: a. Is the image erect or inverted b. Is the image real or virtual? c. Is it enlarged, diminished, or the same size?arrow_forwardA converging (concave) mirror with a focal length of 7 cm is held 4 cm from your face. a. Determine the image location. Insert your solution here: b. What is the magnification of the image? Use the formula belowarrow_forward
- You will need a straightedge and a protractor for both problems on this homework. 1. Image Formation by a Cylindrical Mirror A pin is placed in front of a semi-cylindrical mirror as shown in the top-view diagram below. Location of observer 1 X Location of observer 2 Mirror Pin omor 16arrow_forwardBelow is a compound microscope. A) BODN lenses and draw your lines on the figure below. Find the image location using ray tracing (geometrical optics). Assume thin h₂=5 cm on your computer? f₁ What are the image features? Calculate the final image location using the thin lens equation (d₂'). What is the magnification (M) of this microscope? Where should you put a digital camera if you want to capture and save the image f₁ = 10 cm (objective) X = 30 cm f₂ f₁ f₂ (eye piece) f₂arrow_forwardconstruct ray diagrams for each marked dot to show the location and appearance of the image. That’s 4-5 ray diagrams per letter. Draw your rays lightly (but visibly) and mark your image points boldly.CONVERGING LENS 1.Where does the image of the letter “A” appear?2. Is the image of the letter A larger, smaller, or the same size as the object?3.Is the image of the letter A upright or inverted?4. In what way is the image of the letter A distorted?arrow_forward
- During a lens lab, Jerome and Michael placed a 4.5-cm tall night light bulb a distance of 42.8 cm from a lens. The image of the light bulb was inverted and appeared 26.5 cm from the lens.a. Determine the focal length of the lens being by Jerome and Michael.b. Determine the expected height of the image of the bulb.arrow_forwardDraw the figure shown abov onto the same page as the mathematical proofs of your answer. Using the upright arrow as your object, draw the three primary light rays (M-, F-, and P-rays) to determine where the image will be located. Finally draw in the image taking care to show the correct size and orientation of the image. The black dots in the diagram represent the focal points of the lens.arrow_forwardLight rays fall normally on the vertical surface of a glass prism (n = 2.05) as shown in Figure. 1) What is the largest value of 0 such that the ray is totally internally reflected at the slanted face? (Express your answer to three significant figures.) Submit 0 2) Repeat the calculation if the prism is immersed in water with n = 1.33. (Express your answer to three significant figures.) Submit O Oarrow_forward
- Problem 2: What is the smallest angle 1 for which a laser beam will undergo total internal reflection on the hypotenuse of the glass prism in figure? a. Draw the refracted and reflected rays inside the glass prism, and the refracted ray as it exits the prism. b. Clearly mark all angles. Show all your calculations here. Ꮎ 30° 60%arrow_forwardThe following problem must be solved making the modifications indicated below. Please read carefully. The figure below shows a thin converging lens for which the radius of curvature have magnitude R1 and R2 respectively. The lens faces a concave spherical mirror that has a radius of curvature of magnitude R.to. Suppose the lens focuses are at a distance F from the lens. Determine its refractive index. b. The lens and mirror are separated by a distance d. An object is placed at a distance L to the left of the lens. Determine the position and magnification of the final image as seen by the eye in the figure. c. Is the image upside down or up? Clearly justify your answer. Modification: Change the converging lens to a diverging lens and assign numerical values to the problem parameters. The questions to be answered are the same (a, b and c). Clearly include the equations used and indicate all of the steps that are necessary to solve the problem. R1 = 40 cm R2 = 90 cm F = 30 cm L = 45…arrow_forward3. Converging Lens - Object Inside Focal Point An object of height 2.5 cm is placed 4.5 cm in front of a converging lens of focal length 15 cm. A. What is the image distance, in cm? Please draw a ray diagram AND use the lens equation to solve algebraically. B. What is the height of the image, in cm? 1 1 1 + = do di f m= Skill: Use 3 Principal Rays to Draw Ray Diagram to Find Image hi ho = - d₁ do Skill: Use Lens Equation to Solve for Image Distance and Image Height Algebraicallyarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





