
Concept explainers
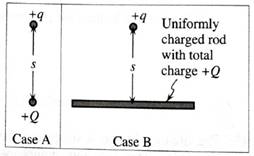
In case A at right, a point Charge
In case B the +q charge is a distance s from the center of an acrylic rod with a total charge
Consider the following student dialogue:
Student 1: "The charge rod and the charged ball have the same charge,
Student 2: "No, in case B there are charges spread all over the rod. The charge directly below the point charge will exert the same force on
Neither student is correct. Discuss with your partners the errors made by each student. Write a correct description of how the forces compare in the space below. Explain.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 5 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Introduction to Electrodynamics
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
- A Two positively charged spheres with charges 4e and e are separated by a distance L and held motionless. A third charged sphere with charge Q is set between the two spheres and along the line joining them. The third sphere is in static equilibrium. What is the distance between the third charged sphere and the sphere that has charge 4e?arrow_forwardA very long line of charge with a linear charge density, , is parallel to another very long line of charge with a linear charge density, 2. Both lines are parallel to the y-axis, and are the same distance r from the y-axis, where the first wire is to the left of the origin and the second is to the right. Use Gausss law and the principle of superposition to find an expression for the magnitude of the electric field at the origin.arrow_forwardSection A, Questions 1 Part (a) of the figure below shows two positive source charges +Q arranged on a semi circu- lar arc of radius r. A test charge +90 is located at the center of the arc. In part (b) of the figure, the two source charges are moved along the circular arc until they are closer to each other. Is the total electro- static force on the test charge qo for part (a) greater than, less, than or equal to the total electrostatic force on the test charge qo for part (b)? +Q (a) (b) +Q +90 +9o +Q +Q rch 75% 7- Cc F3 F4 FS F6 F7 F8 F10 F11 PrtSc F12 %23 24 5 8 9. T Y. G H. K M FLarrow_forward
- Two neutral metal spheres on wood stands are touching. A negatively charged rod is held directlyabove the top of the left sphere, not quite touching it. While the rod is there, the right sphere ismoved so that the spheres no longer touch. Then the rod is withdrawn. Afterward, what is the charge.state of each sphere? Use charge diagrams to explain your answer.arrow_forwardA negatively-charged balloon is brought near a neutral, conducting sphere (mounted on an insulating stand). The sphere is touched by a person and the balloon is moved away. Question 1: What is the charge on the balloon after? (positive, negative, neutral) Explain. What is the charge on the metal sphere? (positive, negative, neutral) (positive, negative, neutral) Explain. 2. A neutral metal can is mounted on a foam stand. A positively charged balloon is brought nearby. The can is touched on the opposite side. Question 1: What is the charge on the balloon after? (positive, negative, neutral) Explain. Question 2: What is the charge on the can? (positive, negative, neutral) Explain.(please provide answers to each questions thank you)arrow_forwardThree point charges are arranged in a horizontal line as shown below. Find the electric force on Q1, Q2, and Q3 given the following: Q1 = 3 uC, Q2 = -1 uC, Q3 = -5 uC, r1 = 100 m, and r2 = 200 m. Remember that a positive force points to the right and a negative force points to the left. What is the net force on charge Q1? Q2? Q3? In newtonsarrow_forward
- If two identical conducting spheres are in contact, any excess charge will be evenly distributed between the two. Three identical metal spheres are labeled A, B, and C. Initially, A has charge q, B has charge −q/2, and C is uncharged. Part A. What is the final charge on each sphere if C is touched to B , removed, and then touched to A ?Express your answers separated by commas in terms of q . Part B.arrow_forwardYou discovered that when two point charges are separated by 8 cm then the attractive force F, between them is 100 N. A. Find the new force Fʹ, between them when they are separated by 2 cm. B. You are given that charge q1 has twice the charge of q2 (i.e. q1 = 2q2). Now calculate the magnitude of both charges. (k = 9 x 109 N.m2C-2).arrow_forwardA small circular plate (2D) has a radial charge distribution of n(r) = (12)r. *. If the plate has a radius of 2cm, how much total charge is on the plate? Since the plate and charge are both radially symmetric, you should use polar coordinates here.arrow_forward
- Two point charges are placed on the x-axis as follows: Charge q1=+4.00nC is located 0.20m,and charge q2=+5.00nC is at x=-0.30m. a.Draw a sketch of te setting discussed in the question above. Make sure to label all points discussed. b. What are the magnitude and direction of the total force exerted by these two charges on a negative point charge q3=-6.00nC that is placed at the origin?arrow_forwardThree point charges are located in free space along the x-axis. A positive charge of +2 uC is located at x = 0, a negative charge of -3 μC is located at x = 3 m, and a positive charge of +4 μC is located at x = 6 m. a. Will q1 and q2 attract or repel? Blank 1 b. Will q1 and q3 attract or repel? Blank 2 c. What is the direction of the electrostatic force acting on q1 due to q2? (north, south, east, or west) Blank 3 d. What is the direction of the electrostatic force acting on q1 due to q3? (north, south, east or west) Blank 4 For the following questions, convert your answer into PROPER SCIENTIFIC NOTATION and round the coefficient to two decimal places.(e.g. 5.43 x 10²: 5.43 is the coefficient) What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on q1 due to q2? Blank 5 x10^Blank 6 N What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on q1 due to q3? Blank 7x10^Blank 8 N Calculate the net electric force on the positive charge at x = 0 due to the other two charges: Blank 9 x 10^Blank 10 Narrow_forwardA charge of -2.50 nC is placed at the origin of an ry-coordinate system, and a charge of 1.65 nC is placed on the y axis at y = 4.45 cm Part A If a third charge, of 5.00 nC , i now placed at the point z = 2.65 cm , y = 4.45 cm find the z and y components of the total force exerted on this charge by the other two charges. Enter your answers in newtons separated by a comma. nν ΑΣφ ? Submit Request Answer Part B Find the magnitude of this force. Express your answer in newtons. ? F = N Submit Request Answer Part C Find the direction of this force.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

