
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.3, Problem 2bT
A second experiment is performed in which glider D is fixed in place. Glider C is launched toward glider D with the same velocity as in the first experiment, and it rebounds with the same speed that it had initially.
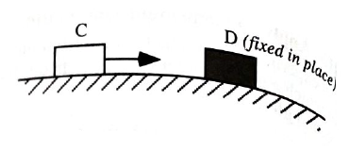
- In the spaces provided, draw separate free-body diagrams for each glider and for the system of the two gliders at an instant during the collision in this second experiment.

Explain how the fact that glider D is fixed in place is reflected in your free-body diagrams.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule07:24
Students have asked these similar questions
Object A traveling east at 4 m/s collides with object B traveling west at 2 m/s. Object A has mass 2 kg and object B has mass 5 kg. The collsion takes place in one dimension, and is elastic. Taking east to be positive, how do I find the final velocity of object A? (Note : There is no given final velocity for object B in the problem) (If you could show a step by step diagram, that would be greatly appreciated, no rush)
During an elastic collision, a proton with a velocity of 5000m/s (forward) undergoes a head on collision with an alpha particle (composed of two protons and two neutrons) with a velocity of 2000m/s (backward). Determine the final velocities of the subatomic particles. Assume forward is positive. Show all your steps please.
A 5-kilogram block slides at 20 m/s on a smooth frictionless surface toward a
stationary sphere, shown below. The sphere is 4 times the mass of the block. The
block strikes the sphere at time t-D0. A plot of the force exerted on the CUBE by
the ball as a function of time is shown above right.
20
20 m
10
a) What is the impulse applied to the block?
Your answer
b) What is the speed of the cube immediately following the collision? (HINT:
Impulse = A momentum)
Your answer
c) What is the velocity of the cube immediately following the collision? (State
both direction and magnitude.)
Your answe
IN
Chapter 3 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 3.1 - A block is moving to the left on a frictionless,...Ch. 3.1 - In a separate experiment, two hands push...Ch. 3.1 - Shown at right is a side-view diagram of the...Ch. 3.1 - Recall the motion of the block in part B. For each...Ch. 3.1 - Generalize from your answers to pans A—D to...Ch. 3.1 - A glider, glider A, Is pulled by a suing across a...Ch. 3.1 - The diagrams at right show two identical gliders...Ch. 3.1 - A block on a frictionless table is connected to a...Ch. 3.2 - Three students discuss the final momentum and...Ch. 3.2 - Which cart takes longer to travel between the two...
Ch. 3.2 - Use Newton's second law and the definition of...Ch. 3.2 - How does the net work done on cart A(Wnet,A)...Ch. 3.2 - Refer again to the discussion among the three...Ch. 3.2 - Release the ball so that it rolls straight toward...Ch. 3.2 - Release the ball at an angle to the ramp as shown...Ch. 3.2 - How does the direction of the net force on the...Ch. 3.2 - How does the change in kinetic energy of the ball...Ch. 3.2 - For motion 1, draw vector in region II of the...Ch. 3.2 - For motion 2, draw vectors in region II of the...Ch. 3.2 - Consider the change in momentum vectors you...Ch. 3.3 - What differences between gliders M and N could...Ch. 3.3 - For experiment 1,draw and label separate free-body...Ch. 3.3 - In the spaces provided, draw and label vectors to...Ch. 3.3 - A student compares the final speeds of gliders M...Ch. 3.3 - A. Suppose that glider D is free to move and...Ch. 3.3 - A second experiment is performed in which glider D...Ch. 3.3 - Consider the two experiments described above. When...Ch. 3.3 - When the momentum of an object or system of...Ch. 3.3 - Two students the second experiment, in which...Ch. 3.4 - Draw separate free-body diagrams for each block...Ch. 3.4 - Rank the magnitudes of all the horizontal forces...Ch. 3.4 - The velocity vectors for blocks A and B are shown...Ch. 3.4 - Use your knowledge of the velocities and changes...Ch. 3.4 - Draw and label a free-body diagram for system C at...Ch. 3.4 - Write an equation for the momentum of system C in...Ch. 3.4 - Generalize from your results to answer the...Ch. 3.4 - Imagine a single object whose mass is equal to the...Ch. 3.4 - What are the external forces exerted on system C...Ch. 3.4 - The momentum vectors of each block before the...Ch. 3.4 - Draw arrows that represent the direction of the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
55. A stone with a mass of 0.100 kg rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface. A bullet of mass 2.50 g travel...
College Physics (10th Edition)
At a middle school talent show, 14-year-old Sam Smally read off the names he had given to each of the 100 billi...
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
1. If a particle’s speed increases by a factor of 3, by what factor does its kinetic energy change?
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Does it ever make sense to say that one object is twice as hot as another? Does it matter whether one is referr...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
In considering the potential of an infinite flat sheet, why isnt it useful to take the zero of potential at inf...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING OF SECTION 13.8 If the sun somehow collapsed to form a black hole, what effect would th...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Correct Two cars, both of mass m, collide and stick together. Prior to the collision, one car had been traveling north at speed 3v, while the second was traveling at speed 2v at an angle o south of east (as indicated in the figure). After the collision, the two-car system travels at speed vfinal at an angle 0 east of north. (Figure 1) Part B What is the angle 0 with respect to north made by the velocity vector of the two cars after the collision? Express your answer in terms of 4. Your answer should contain an inverse trigonometric function using the notation asin, atan etc. and not arcsin, arctan etc. Tigure 1 of 1 > View Available Hint(s) Πν ΑΣφ 2v Vfinal = 3v Submit E Provide Feedback Nextarrow_forwardPart A Block 1, of mass mi 9.50 kg, moves along a frictionless air track with speed t 25.0m/s.t collides with block 2, of mass ma 13.0 kg. which was initially at rest. The blocks stick together after the collision. (Elgure 1) Find the magnitude p of the total initial momentum of the two-block system. Express your answer numerically. > View Avallable Hint(s) ? Pi= kg m/s Figure 1 of 1 Submit Before collision: m2 Part B Find vr, the magnitude of the final velocity of the two-block system. Express your answer numerically. > Vlew Available Hint(s) After collision: Vo AEd m/s • Previous MacBook Pro G Search or type URL & # $ % @ 8. 3 4 R Y W E H K F S N V Barrow_forwardA tie of uniform width is laid out on a table, with a fraction of its length hanging over the edge. Initially, the tie is at rest. (a) If the fraction hanging from the table is increased, the tie eventually slides to the ground. Explain. (b) What is the coefficient of static friction between the tie and the table if the tie begins to slide when one-fourth of its length hangs over the edge? Show your work and explain.arrow_forward
- Disk P (inertia 0.41 kg ) moves at an unknown velocity across a low-friction horizontal surface and collides with disk Q (inertia 0.75 kg ), which is initially at rest. After the collision, the two (now slightly dented) disks move apart without spinning. Velocity information is provided in the initial and final top-view diagrams in the (Figure 1). Part A What was the initial velocity of disk P? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? Value Units Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 7 attempts remaining Part B What fraction of the initial kinetic energy is converted during the collision? Πν ΑΣφ Kị-K _ Figure < 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer initial final < Return to Assignment Provide Feedback 1.4 m/s 20° Qat rest /50° (P not shown) 0.96 m/sarrow_forwardA 22-g bullet traveling 240 m/s penetrates a 2.0-kg block of wood and emerges going 150 m/s. If the block is stationary on a frictionless surface when hit, how fast does it move after the bullet emerges? please show your work, including diagrams, algebraic equations, and enough written explanations that somebody who is not familiar with the problem could understand what you are doing.arrow_forwardShow all of your work. A 50 kg box is being pulled to the right across the floor as shown. a) Describe two free body diagrams: one without resolving components, and one with (only) resolved components. b) Apply Newton’s 2nd Law along the x-direction. Calculate the acceleration of the box along the floor. c) Apply Newton’s 2nd Law along the y-direction. Calculate the normal force upon the box.arrow_forward
- Center of mass of constant-density plates Find the center of mass (centroid) of the following thin, constant-density plates. Sketch the region corresponding to the plate and indicate the location of the center of mass. Use symmetry whenever possible to simplify your work. The region bounded by y = sin x and y = 0 between x = 0 and x = πarrow_forwardA 5 kg sphere moves at 5m/s in the +x direction and hits a 2kg stationary ball at the origin. After the spheres collide, the lighter ball has a final velocity of 3.6m/s directed 49 degrees from the x axis as shown in the image below. 1. Figure out the speed (v') and direction (theta) of the heavier ball after the collision 2. Is the collision elastic or inelastic? Explain your answer in 3 sentences or less. 5 kg 5 m/s 2 kg To 49° 3.6 m/s Iarrow_forwardFor the left figure below, replace the distributed loads by an equivalent resultant force and a couple moment acting at point A. (See the right figure below.) Let a = 4.00 m, w₁=5.00 kN/m, and ₂ = 4.55 kN/m. Calculate the resultant force, FR. and the couple moment, MR,A. Don't forget to include the appropriate signs (consistent with the right figure) with your numerical answers. Express your answers numerically in kilonewtons and kilonewton-meters to three significant figures separated by a comma. View Available Hint(s) FR, MR,A= IVD| ΑΣΦ | vec ? B kN, kN.m MRAarrow_forward
- с u 3 ÏÎ Stotoarrow_forwardCenter of mass of constant-density plates Find the center of mass (centroid) of the following thin, constant-density plates. Sketch the region corresponding to the plate and indicate the location of the center of mass. Use symmetry whenever possible to simplify your work. The region bounded by y = x3 and y = x2 between x = 0 and x = 1arrow_forwardA box A, having a mass of 20 kg, is released from rest at the position shown in (Figure 1) and slides freely down the smooth inclined ramp. When it reaches the bottom of the ramp, it slides horizontally onto the surface of a 50-kg cart for which the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cart and the box is μ = 0.6. Part A If h = 0.4 m, determine the final velocity of the cart once the block comes to rest on it. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = 0.800 ™ Figure 2.5 m 1 of 1 Submit Previous Answers Part B Correct Also, determine the positions of the box on the cart after it comes to rest on the cart. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ΜΑ ? 8 = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON