
Interpretation:
The purine and pyrimidine ring structures should be drawn demonstrating the
Concept Introduction:
Heterocyclic
Explanation of Solution
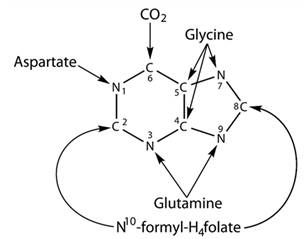
Purine is represented in a double-ring structure which has four-nitrogen and five-carbon atoms. In this structure, carbon-2 and carbon-8 are obtained from N10 -formyl −H4folate and nitrogen-3 and nitrogen-9 are obtained from glutamine. There is no metabolic relation between purine and pyrimidines. Purine and Pyrimidines both have a different process for the synthesis and for the degradation. These both process of degradation and synthesis occur in all organisms. Structure of the purine is given below-
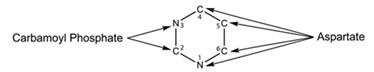
Pyrimidine is a six-membered single ring structure. It has two nitrogen and four carbon atoms. Nitrogen-3 and carbon-2 are obtained from carbamoyl phosphate. Carbon-4,5,6 and nitrogen-1 are obtained from aspartate. Structure for the pyrimidine is given below-
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Biochemistry
- The four-carbon sugar erythrose-4-phosphate is the starting material in the synthesis of many compounds. Name two important examples.arrow_forwardDraw the enediolate intermediate of the ribulose-5-phosphate isomerasereaction (Ru5P → R5P).arrow_forwardA reaction involved in the metabolism of sugars is the splitting of fructose-1,6-diphosphate to give glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. In the living system, this retro-aldol is catalyzed by an enzyme called aldolase; however, it can also be catalyzed by a mild base. Propose a mechanism for the base-catalyzed reaction. CH,-0-P-0- CH,-0-P-0- C=0 C=0 CH,OH dihydroxyacetone phosphate HO-C-H aldolase or "OH H-C-OH H-C-OH H-C-OH CH,-0-P-0- CH2-0-P-0- fructose-1,6-diphosphate glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatearrow_forward
- this drug contains one or more building blocks derived from either ethylene oxide or epichlorohydrin.Identify the part of each molecule that can be derived from one or the other of the building block and propose structural formulas for the nucleophile(s) that can be used along with either ethylene oxide or epichlorohydrin to synthesize each molecule.arrow_forwardWhat is the biochemical rationale for the isomerization of glucose 6- phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate and its subsequent phosphorylation to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate?arrow_forward(i) Describe the mechanism of chymotrypsin in cleaving a peptide bond, highlighting the roles of the catalytice triad for the two phases of the catalytic reactions. Explain the significance of the oxyanion hole for the catalysis. (ii) All serine proteases contain the catalytic triad and these amino acids are positioned in the exact same conformation. Since this is true, why do trypsin and chymotrypsin have such different substrate specificity? What features of the enzyme allow for this situation?arrow_forward
- Refer to the reaction scheme of the GAPDH catalyzed formation of 1,3-BPG. In the reaction, the nucleophile in step (4) is an inorganic phosphate molecule. The enzyme active site is elaborately constructed so that inorganic phosphate, not water, acts as the nucleophile. What advantage is gained by using inorganic phosphate, instead of water, as the nucleophile? Discuss in terms of the energy yield of glycolysis. No need to calculate the total net energy yield of glycolysis.arrow_forwardThe amount of branching (number of (α1→6) glycosidic bonds) in amylopectin can be determined by the following procedure. A sample of amylopectin is exhaustively methylated—treated with a methylating agent (methyl iodide) that replaces the hydrogen of every sugar hydroxyl witha methyl group, converting —OH to —OCH3 . All the glycosidic bonds in the treated sample are then hydrolyzed in aqueous acid, and the amount of 2,3-di-O-methylglucose so formed is determined.(a) Explain the basis of this procedure for determining the number of (α1→6) branch points in amylopectin. What happens to the unbranched glucose residues in amylopectin during the methylation and hydrolysis procedure?(b) A 258 mg sample of amylopectin treated as described above yielded 12.4 mg of 2,3-di-O-methylglucose. Determine what percentage of the glucose residues in the amylopectin contained an (α1→6) branch. (Assume that the average molecular weight of a glucose residue in amylopectin is 162 g/mol.)arrow_forwardDraw the first tetrahedral intermediate of the chymotrypsin mechanism (a single structure, no arrows required). Circle the oxyanion hole. How does the oxyanion hole of chymotrypsin compare to that of carboxypeptidase?arrow_forward
- Suppose a polymer of glucose with alternating α(1-->4) and β(1-->4) glycosidic linkages has just been discovered. Draw a Haworth projection for a repeating tetramer (ie, two repeating dimers) of such a polysaccharide. What organism might use this as a food source?arrow_forwardConsider the reaction for assembly of a tetrapeptide from four amino acids: Serine + Proline + Alanine + Methionine ----> SPAM tetrapeptide Draw a free energy diagram for this reaction (you know, the one that is a line with a speed bump on it?). Remember to always label the axes on graphs, and label where the (actual) reactants and products free energies are on the curve. In addition, label activation energy and draw a dashed line showing the effect of an enzyme on the curve.arrow_forwardLooking at the structure of alpha linolenic acid and knowing the electron carriers produced in each round of traditional beta oxidation for saturated fatty acid chains, how many rounds of beta oxidation will have diminished production of electron carriers due to the presence of double bonds?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
