
Concept explainers
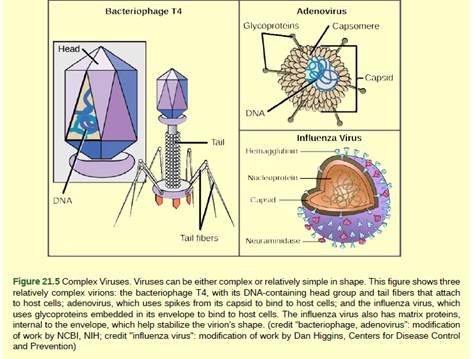
Figure 21.5 Which of the following statements about virus structure is true?
- All viruses are encased in a viral membrane
- The capsomere is made up of small protein subunits called capsids.
Introduction:
Viruses have diversity in terms of the structure, the method of replication, host and target cells. Viruses are non-cellular and parasitic and do not have any internal organelles, metabolic process or plasma membrane. The virion consists of a nucleic acid core of either DNA or RNA, an outer coating of protein, or sometimes may have an outer membrane which is made up of phospholipid membrane which is derived from the host cell and proteins.
Answer to Problem 1VCQ
Correct answer:
The correct answer is option (d) Glycoproteins help the virus attach to the host cell.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/justification for the correct answer:
Option (d) Glycoproteins help the virus attach to the host cell. All the virions have the nucleic acid genome which is covered with an outer protein protective layer is termed as capsid. Capsomere is small protein subunits that make up the capsid. The capsid of some of the viruses has a surrounding outer structure which is the viral envelope.
All the viruses contain some kind of the glycoprotein for attachment to the host cell molecules which are the viral receptors. These cell surface molecules are exploited by viruses for recognition and infection to particular types of cell. So, the correct answer is option (d).
Explanation for the incorrect answer:
Option (a) All viruses are encased in a viral membrane. Viruses may or may not have a viral membrane. So, this is an incorrect option.
Option (b) The capsomere is made up of small protein subunits called capsids Capsomere are small protein subunits that make up the capsid. So, this is an incorrect answer.
Option (c) DNA is the genetic material in all viruses. The virion consists of a nucleic acid core of either DNA or RNA. So, this is an incorrect answer.
All the viruses contain some kind of the glycoprotein for attachment to the host cell molecules which are the viral receptors. These cell surface molecules are exploited by viruses for recognition and infection to particular types of cell. Hence, the correct answer is option (d) Glycoproteins help the virus attach to the host cell.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Biology 2e
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics
Human Anatomy & Physiology
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (10th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (6th Edition) - standalone book
- The genome of a virus consists of (a) DNA (b) RNA (c) prions (d) DNA and RNA (e) DNA or RNAarrow_forwardArrange the following list into the correct sequence for part of the cycle of a retrovirus: 1. dsDNA integrated into host DNA 2.viral proteins synthesized on host ribosomes 3. viral DNA uses host enzymes to transcribe viral RNA 4. reverse transcriptase catalyzes synthesis of ssDNA 5. synthesis of second DNA strand (a) 5, 2, 1, 3, 4 (b) 5, 2, 3, 4, 1 (c) 4, 5, 1, 3, 2 (d) 4, 1, 2, 3, 5 (e) 2, 1, 3, 4, 5arrow_forwardFigure 17.6 Influenza virus is packaged in a viral envelope, which fuses with the plasma membrane. This way, the virus can exit the host cell without killing it. What advantage does the virus gain by keeping the host cell alive?arrow_forward
- Arrange the following list into the correct sequence for viral reproduction: 1. penetration 2. assembly 3. replication 4. attachment 5. release (a) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (b) 5, 2, 3, 4, 1 (c) 4, 1, 3, 2, 5 (d) 4, 1, 2, 3, 5 (e) 3, 1, 2, 4, 5arrow_forwardA scientist discovers a new virus with a linear, RNA genome surrounded by a helical capsid. The virus is most likely a member of which family based on structure classification? Rabies virus Herpesviruses Retroviruses Influenza virusesarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true about capsid? There could be more than one answer. Present in both enveloped and naked virus. Composed of individual protein molecules called capsomeresiral nucleic acid. Houses the viral nucleic acid. Capable of self-assembly. Not present in coronavirusarrow_forward
- Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of viruses? they are smaller than prokaryotic cells Othey are acellular (no cellular structure) they are obligatory parasites. Othey are visible with a light microscope Savedarrow_forwardSelect all the correct statement(s) about viruses: Viruses exist in one phase both extracellularly and intracellularly Some viruses are non-obligate parasites Any viral genome can be directly translated by the host cell's translation machinery Viruses can be classified based on their nucleic acid and shapearrow_forwardWhich type of virus would not need a viral enzyme for transcription? retrovirus ds RNA ss (+) sense RNA s (-) sense RNAarrow_forward
- produce a diagram of the replication of a viral genome of stranded RNA simple [+] and mRNA production via Reverse Transcriptase. Produce a diagram of the replication and early maturation of a virus wrapped Produce a diagram of the replication and early maturation of a virus naked. Produce a diagram of the release of an enveloped virus by budding.arrow_forwardGenerally, the DNA viruses have larger genomes than the RNA viruses. How would size be a factor in the manner in which they use the resources of their host cells?arrow_forwardDuring infection of a cell by Coronavirus, the N protein is: found on the outer surface of the virus particles synthesized on bound ribosomes on the rough ER synthesized in the cytosol on free ribosomes part of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase required for binding of the virus particle to cellsarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning



