
(a)
Interpretation:
The given set of solution should be identified as either acidic or basic solution, and the value of 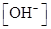 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
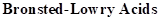 : If a species loses a proton then it is considered as
: If a species loses a proton then it is considered as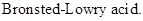
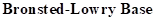 : If a species receives one proton, then it is considered as
: If a species receives one proton, then it is considered as 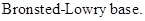
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Ionic-product constant for water: It is the hydronium ion concentration times the 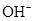 concentration present in the solution.
concentration present in the solution.
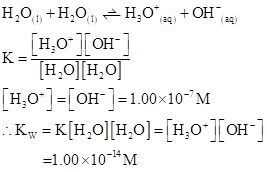
The 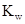 will apply to all aqueous solution.
will apply to all aqueous solution.
For acidic solution 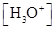 is large that is
is large that is 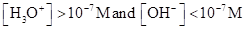
For basic solution 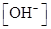 is large that is
is large that is 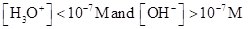
(b)
Interpretation:
The given set of solution should be identified as either acidic or basic solution and the value of 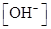 should be determined.
should be determined.
Concept introduction:
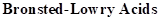 : If a species loses a proton then it is considered as
: If a species loses a proton then it is considered as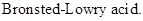
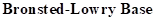 : If a species receives one proton, then it is considered as
: If a species receives one proton, then it is considered as 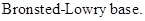
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Ionic-product constant for water: It is the hydronium ion concentration times the 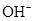 concentration present in the solution.
concentration present in the solution.
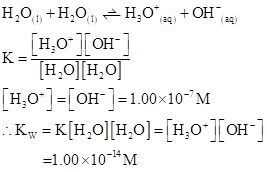
The 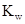 will apply to all aqueous solution.
will apply to all aqueous solution.
For acidic solution 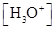 is large that is
is large that is 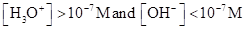
For basic solution 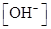 is large that is
is large that is 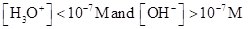
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Determine the pH for the following solutions. {H3O+}=2.4x10^-2 Marrow_forwardPotentiometric titration curve is given below, which is obtained during the potentiometric titration between strong base KOH (0.2 M) with strong acid HI, label the point in the curve from the following options. If more than one points are present than write as x, y(means separate by using comma) a)The point where pH is because of excess OH - ions. b) The point where pH is only because of HI in water. c)The point where [HI]= [I] in water. d)The point where pH=pka e) The point where all HI is neutralized. f) The point where pH corresponds to solution of [I- ] in water. 14 13 12 11 10 9 pH 6. TITIT TITarrow_forwardConsider the following acids and their ionization constant, determine which conjugate base is HCOOH Ka = 1.7 x 10-4 (b) HCN Ka = 4.9 x 10-10arrow_forward
- How many milliliters of 0.125 M sulfuric acid are required to exactly neutralize 25.0 mL of 0.0850 M NH3 solution? Write a balanced reaction.arrow_forwardAn unknown mixture is known to contain only Ba(OH)2 (MW=171.34 g/mole) and NaOH (MW=40.0 g/mole). If the mixture is known to contain 45% by mass NaOH, and 8.0 grams of the mixture is dissolved completely in 50.0 ml of solution, answer the following. c).If 10.0 ml of a 0.2 M solution of Na2SO4 was added to the 50.0 ml solution, what would be the final concentration of Na+ in solution.arrow_forwardDetermine the weight/volume of the chemicals needed to prepare the following solutions: a) 100 ml of 0.9% (w/v) saline (NaCl) b) 30 ml of 50% glycerol (v/v) c) Electrophoresis requires TAE, which is a specific mixture of Tris base, acetic acid, and EDTA. TAE is normally made as a 50X concentrated stock. Provide a recipe to make 40 ml of 50X TAE. The recipe for one liter of 50X TAE is as follows: 242g Tris base, 57.1 ml glacial acetic acid, 100 ml 0.5 M EDTAarrow_forward
- Calculate the normality of a solution that contains 4.5 g of (COOH)2 in 3000 mL of solution? (Assume the (COOH)2 is to be completely neutralized in an acid-base * reaction.) 0.033 N O 0.33 N O 0.166 N O 0.0166 N 0.45 N O 0.045 N 000.0 OOarrow_forwardA 1.000-g sample containing bromide was dissolved in sufficient water to give 100.0 mL. A 50.00 mL aliquot was measured and after acidification, silver nitrate was introduced to precipitate AgBr, which was filtered, washed, and then dissolved in an ammoniacal solution of potassium tetracyanonickelate(II): Ni(CN)42- + 2AgBr(s) → 2Ag(CN)2- + Ni2+ + 2Br- The liberated nickel ion required 11.70 mL of 0.002146 M EDTA. The other 50.00 mL remaining solution was also analyzed for its Br- content by potentiometry using a metallic electrode of the second kind. e) Write the cell notation of the potentiometric set-up with SCE as the reference electrode. f) Write the Nernst equation that describes the indicator electrode set-up.arrow_forwardWhat mass of sodium glycolate (NaC2H3O3) should be added to 400.0 mL of 1.00 M glycolic acid to produce a buffer solution with a pH of 4.00? Ka = 1.47 x 10-4. Please indicate the full solutions.arrow_forward
- What is the pH of stomach acid, a solution of HCl with a hydronium ion concentration of 1.2 × 10−3 M?arrow_forward75 mL of 0.300 mol/L sodium phosphate solution is combined with 67.5 mL of 0.350 mol/L calcium bicarbonate. a)Before you begin your reaction, you must accurately produce 1.500 L of your sodium phosphate solution from sodium phosphate trihydrate solid. Write out a procedure to explain all the steps you will take in the lab when making the solution to ensure that your solution concentration is accurate. Please include calculations that show the required mass of solid. Also include the correct names of all equipment used. b)You have a super powerful microscope in your lab! You are able to zoom in on your sodium phosphate solution and take a picture at the molecular level. Label the diagram on the left with the correct choices from the box on the right. You may use arrows or rewrite the symbols in one appropriate place. c)In one sentence, explain what the diagram is showing.arrow_forwardThe pOH of a basic solution is 3.75. What is [H⁺]?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





