
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305387102
Author: Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.6P
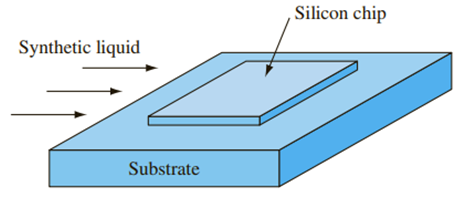
A square silicon chip
Problem 1.6
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Let's say a 3.0 gram copper wafer is dropped from a height of 50.0 meters. If 60% of the potential energy lost in the drop could be converted to thermal energy used to heat the copper from an initial temperature
of 25 degrees celsius, what would the final temperature of the copper wafer?
Would the answer be different if the wafer has a mass greater than 3 grams?
Note: the specific heat of copper is 387 J/(kg*K).
The temperature is between 25.8 and 26.0 degrees celsius, yes the bigger the mass the greater the energy.
O The temperature is between 25.6 and 25.8 celsius, answer does not depend on mass.
O The temperature is between 25.0 and 25.2 celsius, answer does not depend on mass.
O The temperature is 25.5 and of course the more mass something has the greater energy will be needed to raise the temperature.
The temperature is 26.2 and if the mass is doubled so will be the change in temperature.
O The temperature is 25.9 degrees celsius and the answer does not depend on mass.
O The…
20-m pipe has an outside diameter of 50 mm. Pipe is insulated with a layer of
asbestos, then followed by a layer of cork. Inside and outside diameter of the
cork is 77 mm and 80 mm, respectively. If the temperature drop from pipe to
cork is 1165°C, calculate the inside diameter of the pipe (mm). The rate of the
heat transfer is 8778 W. The thermal conductivity of steam pipe, asbestos and
cork are 0.045 kW/m-K, 0.058 W/m-K and 0.043 W/m-K respectively.
The rate at which energy must be dissipated away from single integrated circuits (computer chips) continues to increase as transitors
continue to shrink in size and more and more computations are being completed in smaller and smaller volumes. The maximum chip
temperature, however, has not changed much over time and remains around Tc = 75 °C. To increase the rate of dissipation of thermal
energy away from a new chip, it is proposed to add a 5 x 5 array of copper pin fins to the chip. Each fin will be individually joined to the
chip surface such that there is a minimal contact resistance between the fin and the chip. The diameter of the fins is df = 1 mm and the
length is Lf = 15 mm. The chip is square, with a side length of W= 15 mm. It is so thin that it can be treated as having a single
temperature. A dielectric liquid flows over the outer surface of the chip and around the fins, with a temperature of T»,f= 20 °C and a
convection coefficient of hf = 1150 W/m²-K. The chip is joined to…
Chapter 1 Solutions
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
Ch. 1 - 1.1 On a cold winter day, the outer surface of a...Ch. 1 - 1.2 The weight of the insulation in a spacecraft...Ch. 1 - 1.3 A furnace wall is to be constructed of brick...Ch. 1 - 1.4 To measure thermal conductivity, two similar...Ch. 1 - To determine the thermal conductivity of a...Ch. 1 - A square silicon chip 7mm7mm in size and 0.5-mm...Ch. 1 - A cooling system is to be designed for a food...Ch. 1 - 1.80 Describe and compare the modes of heat loss...Ch. 1 - Heat is transferred at a rate of 0.1 kW through...Ch. 1 - 1.10 A heat flux meter at the outer (cold) wall of...
Ch. 1 - 1.11 Calculate the heat loss through a glass...Ch. 1 - 1.12 A wall with a thickness is made of a...Ch. 1 - 1.13 If the outer air temperature in Problem is...Ch. 1 - Using Table 1.4 as a guide, prepare a similar...Ch. 1 - 1.15 A thermocouple (0.8-mm-diameter wire) used to...Ch. 1 - Water at a temperature of 77C is to be evaporated...Ch. 1 - The heat transfer rate from hot air by convection...Ch. 1 - The heat transfer coefficient for a gas flowing...Ch. 1 - 1.19 A cryogenic fluid is stored in a...Ch. 1 - A high-speed computer is located in a...Ch. 1 - 1.21 In an experimental set up in a laboratory, a...Ch. 1 - 1.22 In order to prevent frostbite to skiers on...Ch. 1 - Using the information in Problem 1.22, estimate...Ch. 1 - Two large parallel plates with surface conditions...Ch. 1 - 1.25 A spherical vessel, 0.3 m in diameter, is...Ch. 1 - 1.26 Repeat Problem 1.25 but assume that the...Ch. 1 - Determine the rate of radiant heat emission in...Ch. 1 - 1.28 The sun has a radius of and approximates a...Ch. 1 - 1.29 A spherical interplanetary probe with a 30-cm...Ch. 1 - A spherical communications satellite, 2 m in...Ch. 1 - A long wire 0.7 mm in diameter with an emissivity...Ch. 1 - Wearing layers of clothing in cold weather is...Ch. 1 - A section of a composite wall with the dimensions...Ch. 1 - A section of a composite wall with the dimensions...Ch. 1 - Repeat Problem 1.35 but assume that instead of...Ch. 1 - 1.37 Mild steel nails were driven through a solid...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.38PCh. 1 - 1.39 On a cold winter day, the outside wall of a...Ch. 1 - As a designer working for a major electric...Ch. 1 - 1.41 A heat exchanger wall consists of a copper...Ch. 1 - 1.43 A simple solar heater consists of a flat...Ch. 1 - A composite refrigerator wall is composed of 5 cm...Ch. 1 - An electronic device that internally generates 600...Ch. 1 - 1.47 A flat roof is modeled as a flat plate...Ch. 1 - A horizontal, 3-mm-thick flat-copper plate, 1-m...Ch. 1 - 1.49 A small oven with a surface area of is...Ch. 1 - A steam pipe 200 mm in diameter passes through a...Ch. 1 - 1.51 The inner wall of a rocket motor combustion...Ch. 1 - 1.52 A flat roof of a house absorbs a solar...Ch. 1 - Determine the power requirement of a soldering...Ch. 1 - 1.54 The soldering iron tip in Problem 1.53...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.55PCh. 1 - A pipe carrying superheated steam in a basement at...Ch. 1 - Draw the thermal circuit for heat transfer through...Ch. 1 - 1.60 Two electric resistance heaters with a 20 cm...Ch. 1 - 1.63 Liquid oxygen (LOX) for the space shuttle is...Ch. 1 - The interior wall of a large, commercial walk-in...Ch. 1 - 1.67 In beauty salons and in homes, a ubiquitous...Ch. 1 - The heat transfer coefficient between a surface...Ch. 1 - The thermal conductivity of fibreglass insulation...Ch. 1 - 1.71 The thermal conductivity of silver at 212°F...Ch. 1 - 1.72 An ice chest (see sketch) is to constructed...Ch. 1 - Estimate the R-values for a 5-cm-thick fiberglass...Ch. 1 - A manufacturer in the United States wants to sell...Ch. 1 - Referring to Problem 1.74, how many kilograms of...Ch. 1 - 1.76 Explain a fundamental characteristic that...Ch. 1 - 1.77 Explain each in your own words. (a) What is...Ch. 1 - What are the important modes of heat transfer for...Ch. 1 - 1.79 Consider the cooling of (a) a personal...Ch. 1 - Describe and compare the modes of heat loss...Ch. 1 - A person wearing a heavy parka is standing in a...Ch. 1 - Discuss the modes of heat transfer that determine...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wall in a house contains a single window. The window consists of a single pane of glass whose area is 0.13 m2 and whose thickness is 8 mm. Treat the wall as a slab of the insulating material Styrofoam whose area and thickness are 19 m2 and 0.10 m, respectively. Heat is lost via conduction through the wall and the window. The temperature difference between the inside and outside is the same for the wall and the window. Of the total heat lost by the wall and the window, what is the percentage lost by the window?arrow_forwardA square silicon chip 7 mm x 7 mm in size and 0.5-mm thick is mounted on a plastic substrate as shown in the sketch below. The top surface of the chip is cooled by a synthetic liquid flowing over it. Electronic circuits on the bottom of the chip generate heat at a rate of 5 W that must be transferred through the chip. Estimate the steady-state between the front and back surfaces of the temperature difference chip. The thermal conductivity of silicon is W 150 mK Silicon chip Synthetic liquid Substratearrow_forward1. Heat Loss from saturated steam at 121.1°C. The line is covered with 25.4 mm of insulation. Assuming that the inside surface temperature of the metal wall is at 121.1°C and the outer sur- face of the insulation is at 26.7°C, calculate the heat loss for 30.5 m of pipe. Also, calculate the kg of steam condensed per hour in the pipe due to the heat loss. The average k for steel from Appendix A.3 is 45 W/m K and the k for the insulation is 0.182. a Steam Pipeline. A steel pipeline, 2-in. Schedule 40 pipe, contains A 381 Stearrow_forward
- The window in my office is 2 metres by 3 metres. Assuming all other walls are well insulated and that heat loss only occurs through the window, calculate what size of heater I need in my office to maintain the temperature, if the inside surface of the glass is at 11 °C and the outside surface at 6 °C. Sketch the temperature profile through the glass. Data: Thickness of glass = 4 mm Thermal conductivity of glass 0.78 W/m K.arrow_forwardIf a heat transfer coefficient of 2.84 W l(m2 • K) exists on each of the two inside faces of two sheets of 6.35-mm-thick glass separated by an air gap, calculate the gap that can be used such that the rate of heat transfer by conduction through the air gap equals the rate of heat transfer by convection. What is the rate of heat transfer if this gap is exceeded. The thermal conductivity of air of 0.0242 WI (m . K). Solve for temperature of 20°C and 12°C on the outside surfaces of the glass. Would the calculated gap change in value for different values of the surface temperatures? Would there be any advantage to increasing the gap beyond this calculated value?arrow_forwardCalculate the quantity of heat conducted per minute through a duralumin circular disc 127 mm diameter and 19 mm thick when the temperature drop across the thickness of the plate is 5 degrees Celsius. Take the coefficient of thermal conductivity of duralumin as 150 W/(m-K).arrow_forward
- The rear window of a car is defrosted by the passage of warm air on the internal surface. If the warm air is at 40 °C and the internal convection transfer coefficient is 30 W/m²°C, what are the temperatures of the internal and external surfaces of the glass (4 mm thick) if the external air temperature is -10 °C and the convection coefficient is 65 W/m²°C?arrow_forwardA pipe carries hot molten lead from one part of a factory floor to another. The mass flow rate of lead is 0.05 kg/s. While trying to figure out the heat loss from the pipe, you found that over a 2-m length of he pipe the lead temperature drops from 580 C to 557.C. What is the rate at which thermal energy is being lost from the lead carrying pipe in this 2-m section? Use the property table to find out properties of lead as needed.arrow_forwardWhat is the rate of heat transfer through a piece of Celotex 3 ft by 8 ft by 1 in. in thickness, if the temp of one surface is 80°F and of the other side is 60°F? thermal conductivity of Celotex in AES = 0.028. Pls determine the temperature gradient and the direction of the heat transfer as well.arrow_forward
- 2. Calculate insulation thickness (minimum value) required for a pipe carrying steam at 180°C. The pipe size is 8" and the maximum allowable temperature of outer wall of insulation is 50 °C. Thermal conductivity of the insulation material for the temperature range of the pipe can be taken as 0.04 W/m K. The heat loss from steam per meter of pipe length has to be limited to 80 W/m. ANSWER: 102.5 mmarrow_forward6. A furnace wall consists of 250 mm fiber brick,125 mm insulating brick, and 250 mm building brick. The inside wall is at a temperature of 600°C and the atmospheric temperature is 20°C. Calculate the heat loss per m' of wall area and the temperature of the outside wall surface of the furnace and the temperature at each interface throughout the wall. The heat transfer coefficient for the outside surface is 10 W/m² °k and the thermal conductivities of the fiber brick, insulating brick and the building brick are 1.4,0.2 and 0.7 W/m.°C respectively.arrow_forwardThe inside surface temperature of a glass oven door (0.5 m x 0.5 m x 0.001 m) is 180°C, the outside surface temperature is 25°C, and the thermal conductivity of glass is 1.4 W/(m•K) What is the rate of heat transfer?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Conduction and the Heat Equation; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6jQsLAqrZGQ;License: Standard youtube license