find the initial pH of 0.2000 L of a buffer solution that is 0.195 M methylamine and 0.125 M methylammonium nitrate, and calculate the pH after the addition of 17.00 mL of 0.550 M potassium hydroxide
find the initial pH of 0.2000 L of a buffer solution that is 0.195 M methylamine and 0.125 M methylammonium nitrate, and calculate the pH after the addition of 17.00 mL of 0.550 M potassium hydroxide
Given : Concentration of methylamine i.e CH3NH2 = 0.195 M
Concentration of methylammonium nitrate i.e CH3NH3NO3 = 0.125 M
Volume of buffer solution = 0.2000 L
Concentration of KOH added = 0.550 M
And volume of KOH solution added = 17.00 = 0.0170 L (since 1 L = 1000 mL)
Initially, the solution is having only weak base CH3NH2 and its conjugate acid CH3NH3NO3 in the solution with the given concentrations.
Hence they will be forming a buffer solution with initial concentrations.
Since the pOH of base buffer is given by Henderson-Hasselbalch equation as,
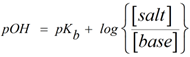
where pKb = 3.36 (using appendix for methylamine)
[salt] = concentration of conjugate acid of base i.e CH3NH3NO3
[base] = concentration of base i.e CH3NH2
Hence substituting the values we get,
=> Initial pH = 14 - pOH = 14 - 3.167 = 10.833 approx.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images









