Answer – In Biology, the letters DNA stand for deoxyribonucleic acid.
Explanation:
DNA is the acronym for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the fundamental genetic material in most living organisms, including some viruses.
The molecule gets its name from the components that make up its structure:
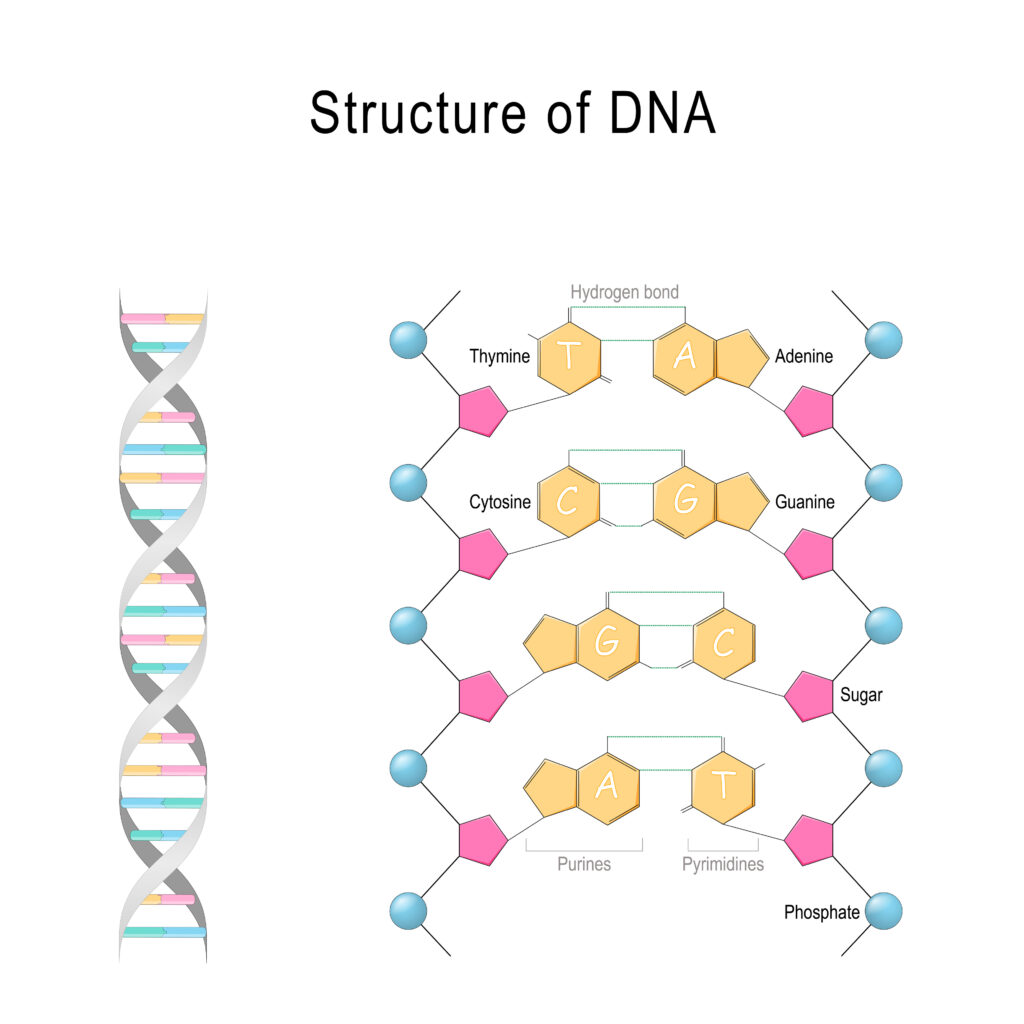
- “Deoxyribo” refers to the pentose, or 5-carbon, sugar called deoxyribose.
- “Nucleic acid” is a reference to the phosphate group and nitrogen bases in the molecule.
The sugar and phosphate group are chemically bonded, forming the ladder-like backbone of DNA. These are linked to the nitrogen bases adenosine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C), which occur in pairs and make up the rungs of the ladder. The base pairs are formed only between A–T and G–C through hydrogen bonds. The resulting structure is a double helix, with each strand running opposite the other in a twisted fashion.
The double helical DNA occurs mostly in the nucleus. Here, it wraps itself around proteins and then around itself several times forming the densely-packed chromatin. This chromatin then undergoes further condensation to form the X-shaped chromosomes, which are responsible for DNA replication during cell division.